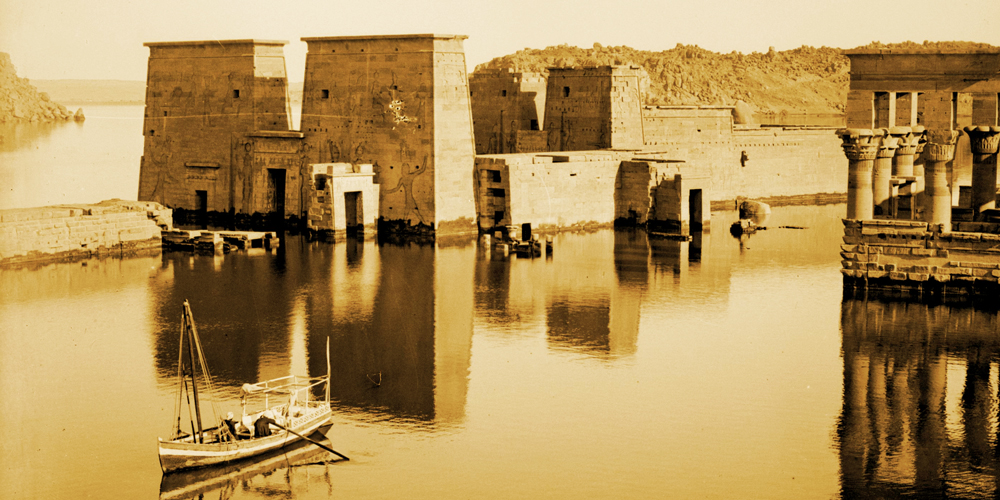
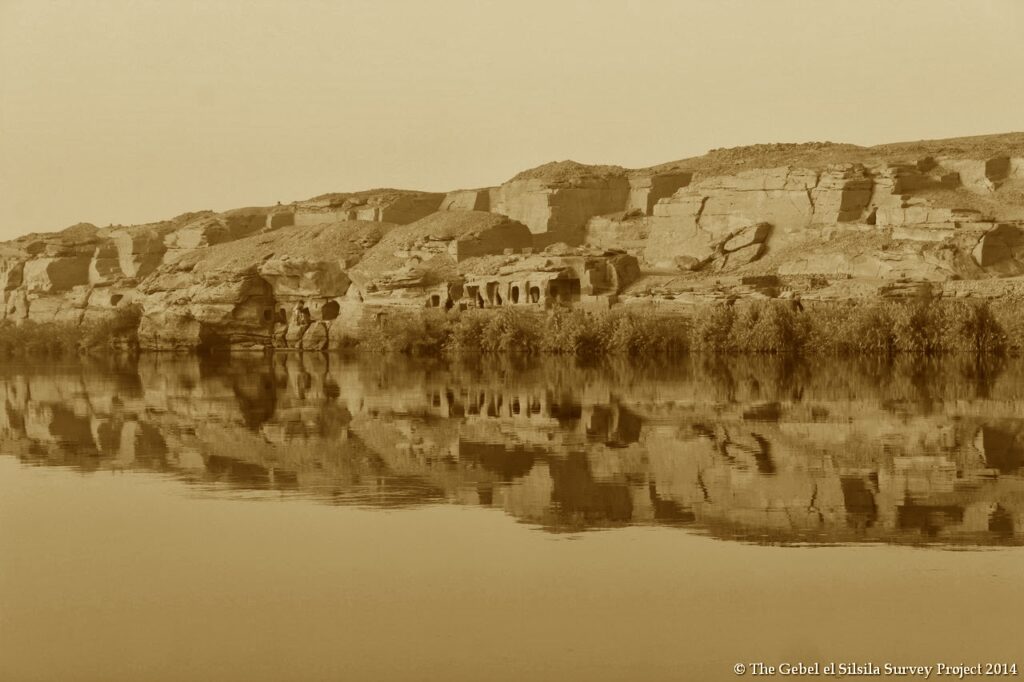
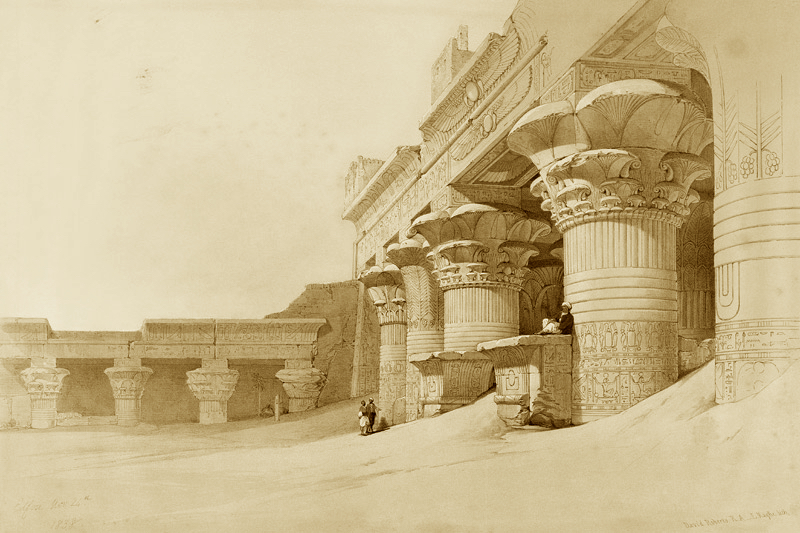
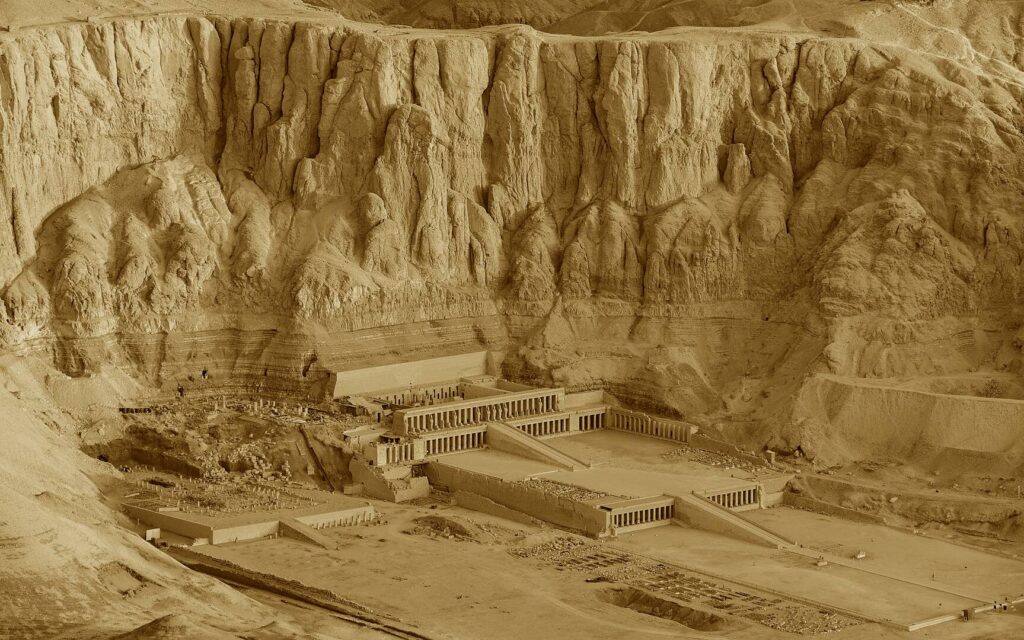
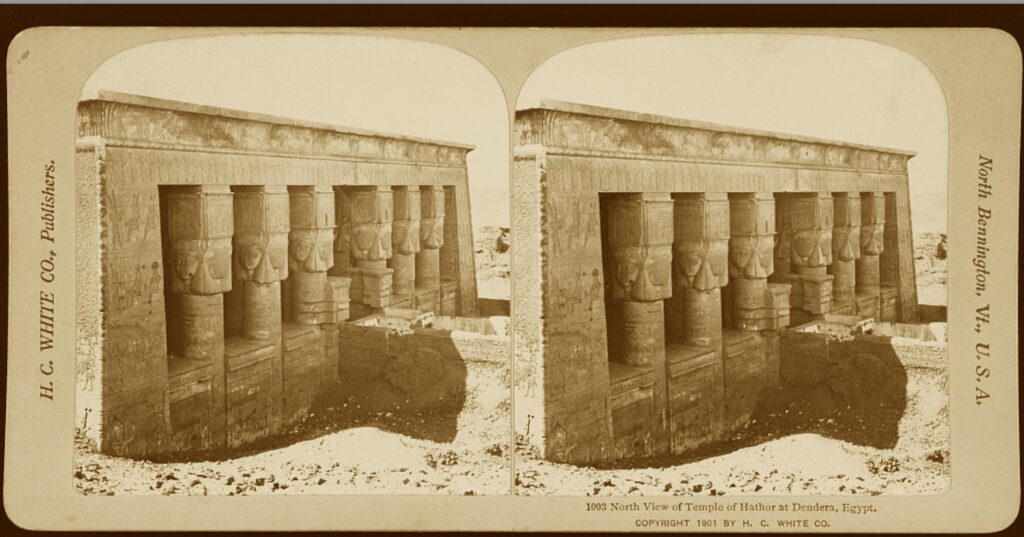
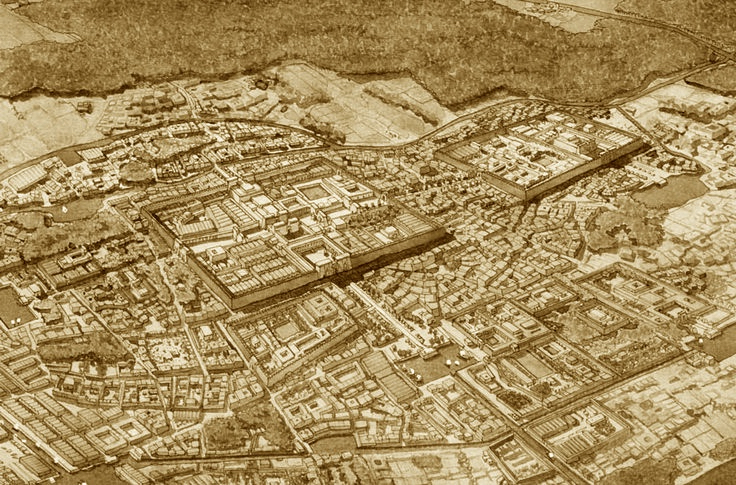
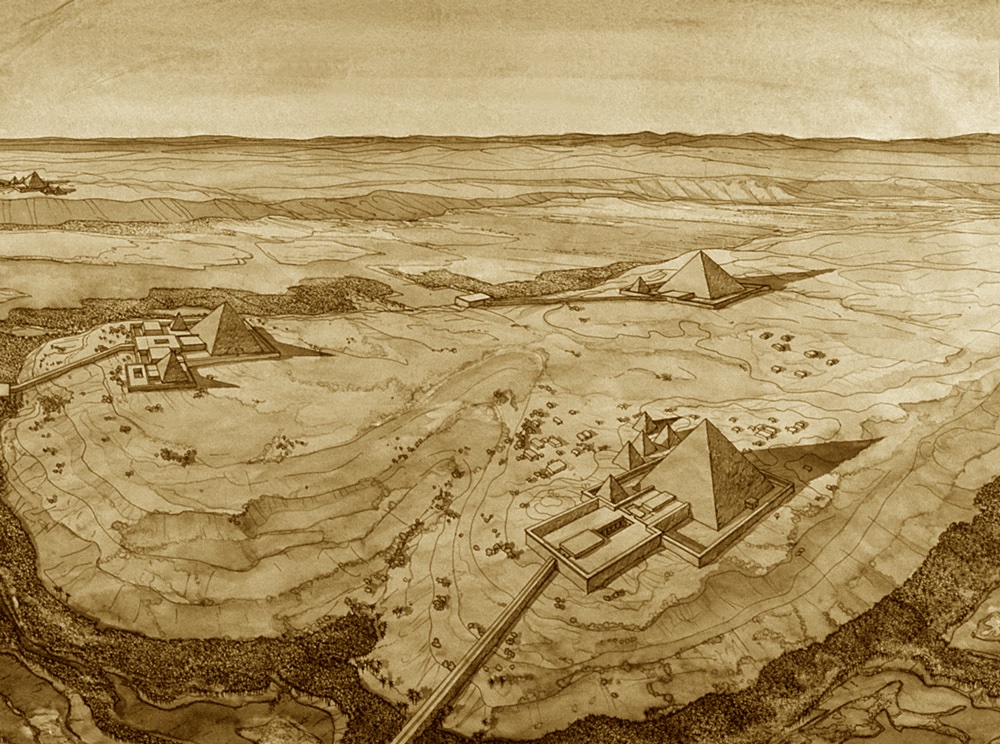
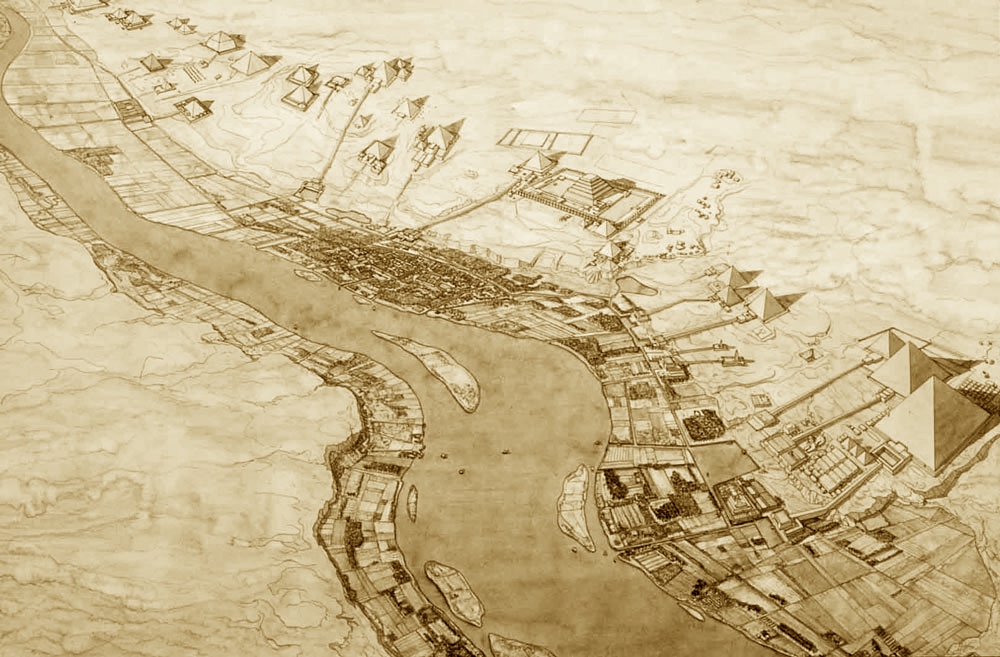
Abu Simbel
Abu Simbel is an ancient temple complex, originally cut into a solid rock cliff, in southern Egypt and located at the second cataract of the Nile River. The two temples which comprise the site were created during the reign of Ramesses II (c. 1279 – c. 1213 BCE) either between 1264 – 1244 BCE or 1244-1224 BCE. The discrepancy in the dates is due to differing interpretations of the life of Ramesses II by modern day scholars. It is certain, based upon the extensive artwork throughout the interior of the Great Temple, that the structures were created, at least in part, to celebrate Ramesses’ victory over the Hittites at the Battle of Kadesh in 1274 BCE. To some scholars, this indicates a probable date of 1264 BCE for the initial construction as the victory would have been fresh in the memory of the people. However, the decision to build the grand monument at that precise location, on the border with the conquered lands of Nubia, suggests to other scholars the later date of 1244 BCE in that it would have had to have been begun after the Nubian Campaigns Ramesses II undertook with his sons and was built as a symbol of Egypt’s power.
Whichever date construction began, it is agreed that it took twenty years to create the complex and that the temples are dedicated to the gods Ra-Horakty, Ptah, and the deified Ramesses II (The Great Temple) and the goddess Hathor and Queen Nefertari, Ramesses’ favourite wife (The Small Temple). While it is assumed that the name, `Abu Simbel’, was the designation for the complex in antiquity, this is not so. Allegedly, the Swiss explorer Burckhardt was led to the site by a boy named Abu Simbel in 1813 CE and the site was then named after him. Burckhardt, however, was unable to uncover the site, which was buried in sand up to the necks of the grand colossi and later mentioned this experience to his friend and fellow explorer Giovanni Belzoni. It was Belzoni who uncovered and first excavated (or looted) Abu Simbel in 1817 CE and it is considered likely that it was he, not Burckhardt, who was led to the site by the young boy and who named the complex after him. As with other aspects regarding Abu Simbel (such as the date it was begun), the truth of either version of the story is open to interpretation and all that is known is that the original name for the complex, if it had a specific designation, has been lost.
The Great Temple stands 98 feet (30 metres) high and 115 feet (35 metres) long with four seated colossi flanking the entrance, two to each side, depicting Ramesses II on his throne; each one 65 feet (20 metres) tall. Beneath these giant figures are smaller statues (still larger than life-sized) depicting Ramesses’ conquered enemies, the Nubians, Libyans, and Hittites. Further statues represent his family members and various protecting gods and symbols of power. Passing between the colossi, through the central entrance, the interior of the temple is decorated with engravings showing Ramesses and Nefertari paying homage to the gods. Ramesses’ great victory at Kadesh (considered by modern scholars to be more of a draw than an Egyptian triumph) is also depicted in detail across the north wall of the Hypostyle Hall. According to the scholars Oakes and Gahlin, these engravings of the events surrounding the battle,