Luxor Museum
The History and Significance of Luxor Museum and the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities
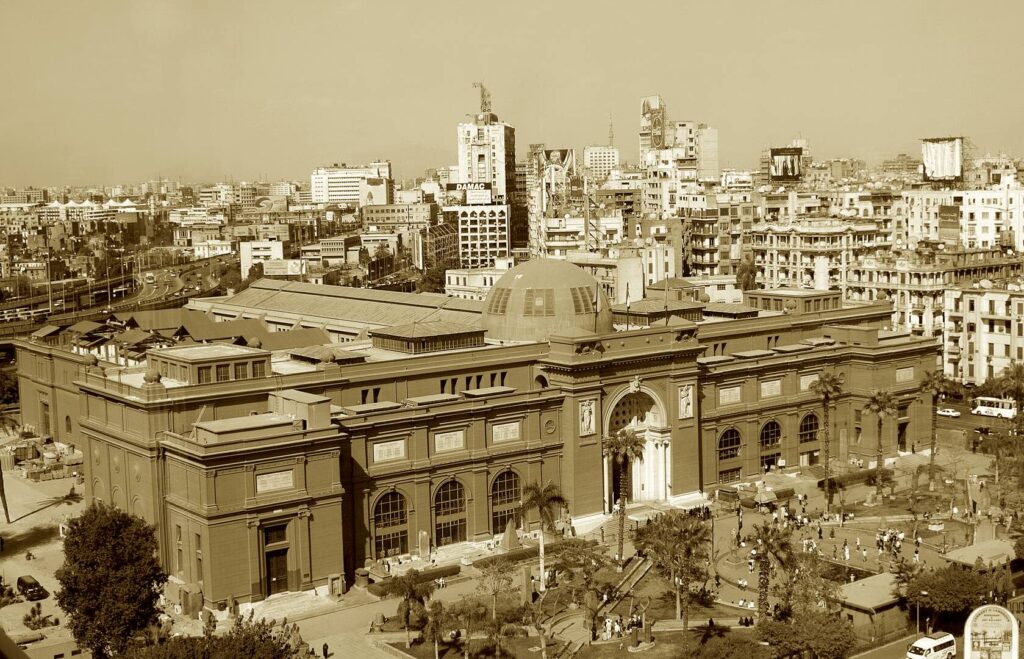
The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, also known as the Egyptian Museum, is one of the world’s greatest repositories of ancient artifacts. Founded in 1835 by the Egyptian government, the museum houses the world’s most extensive collection of Pharaonic antiquities, including the fabulous treasures of Tutankhamun.
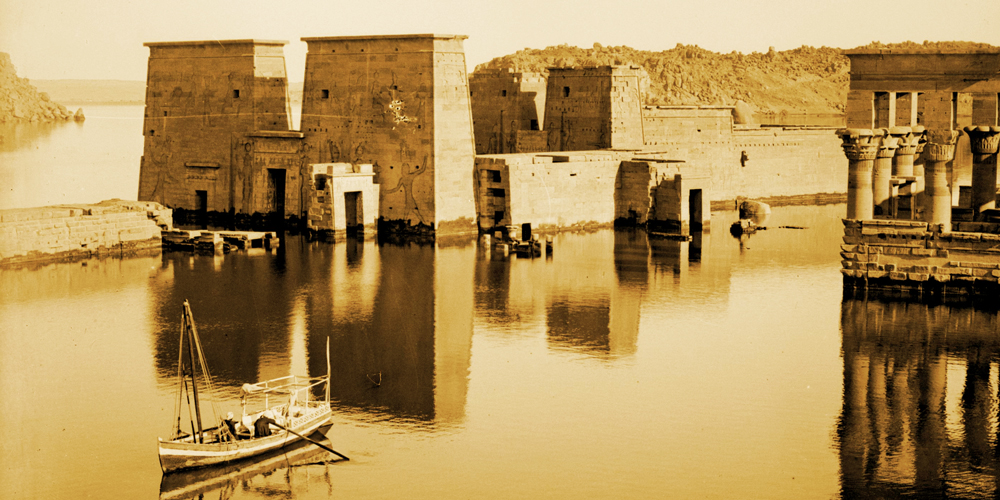
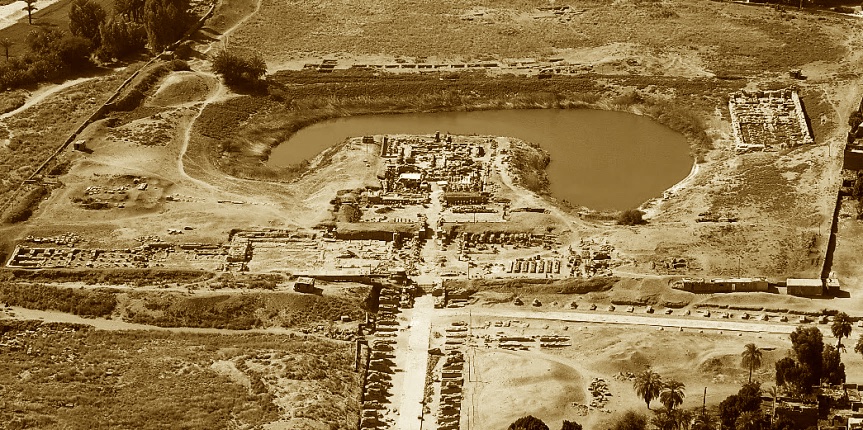
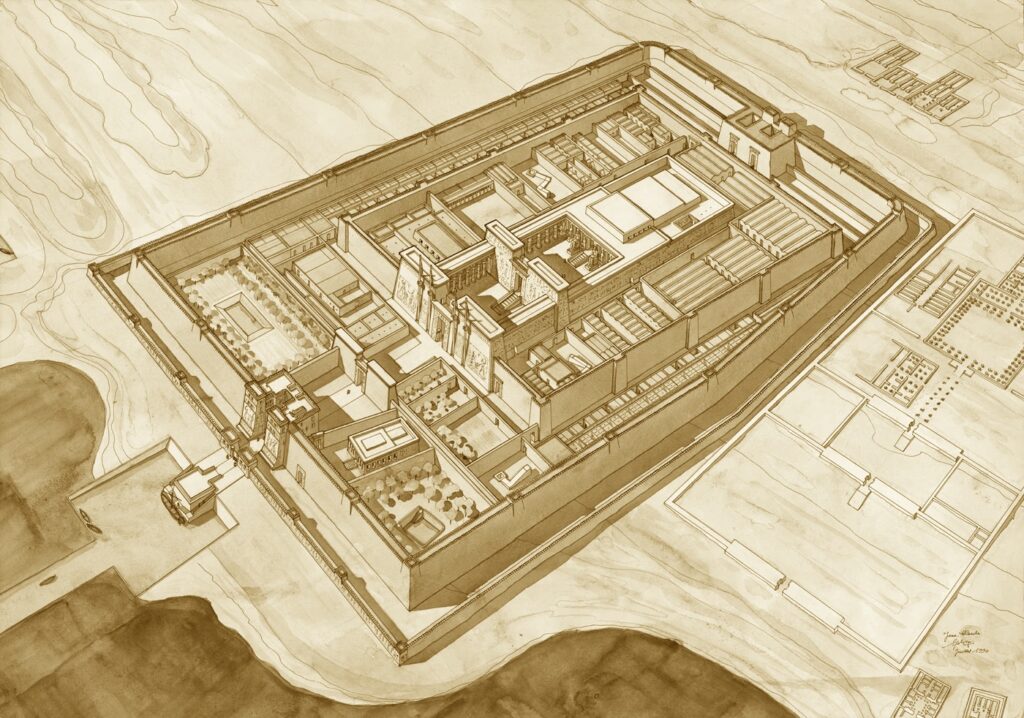
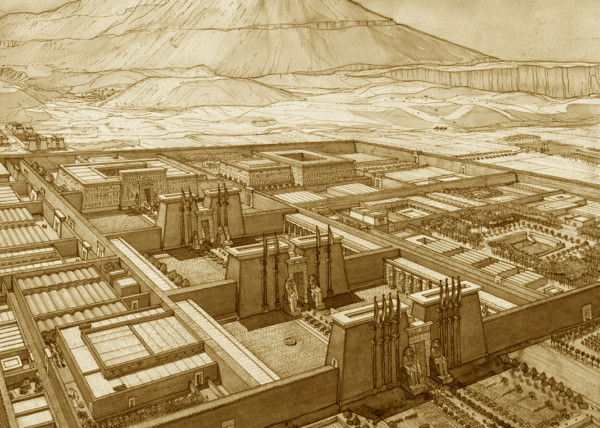
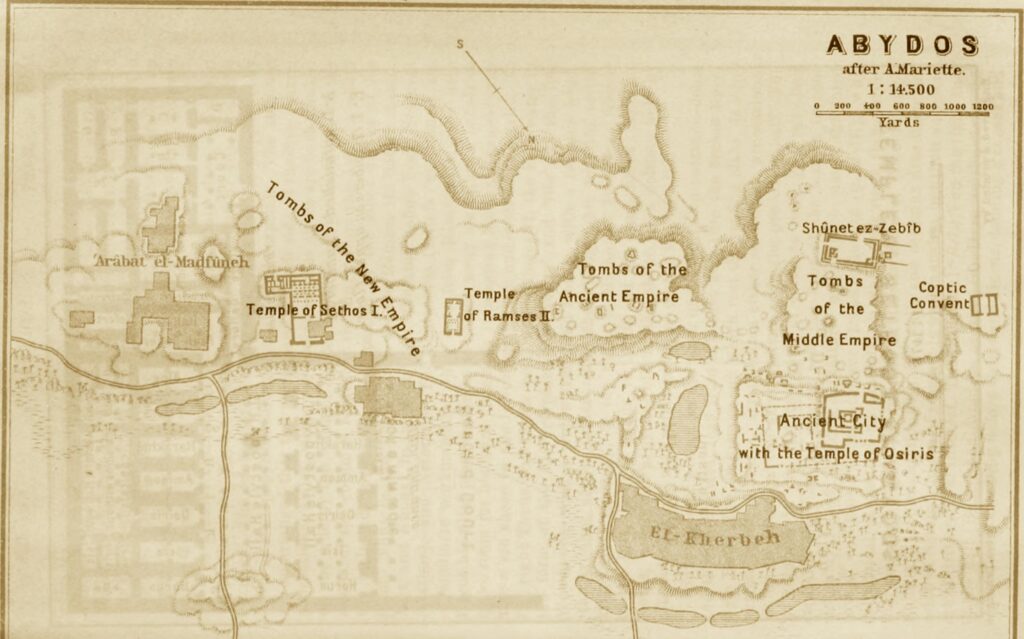
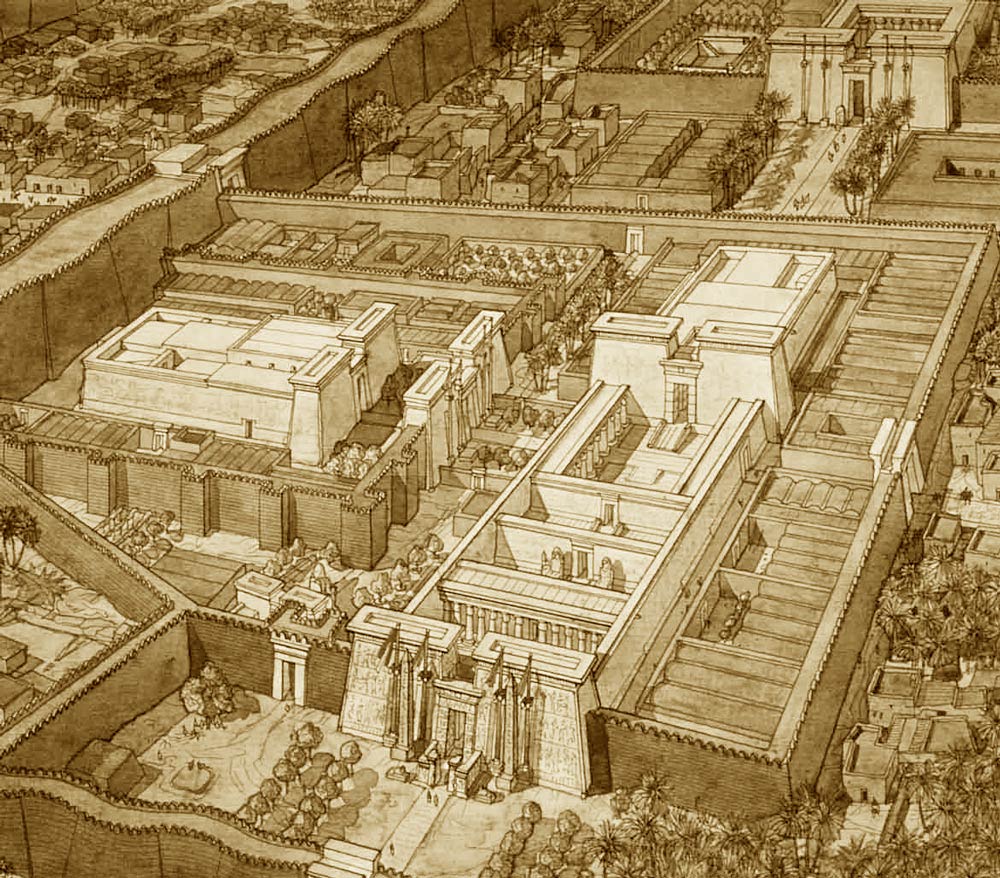
On the other hand, the Luxor Museum, established in 1975, is a beacon of Egypt’s illustrious history. Despite being smaller than its Cairo counterpart, it holds a carefully curated selection of artifacts from the Theban area, which spans different eras of Egyptian history.
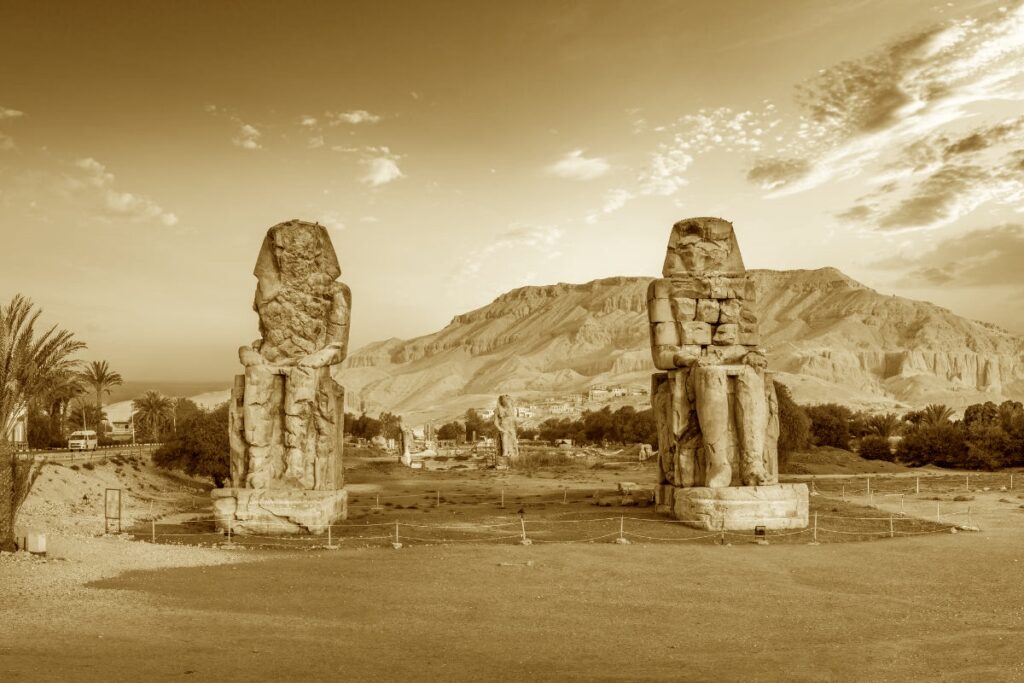
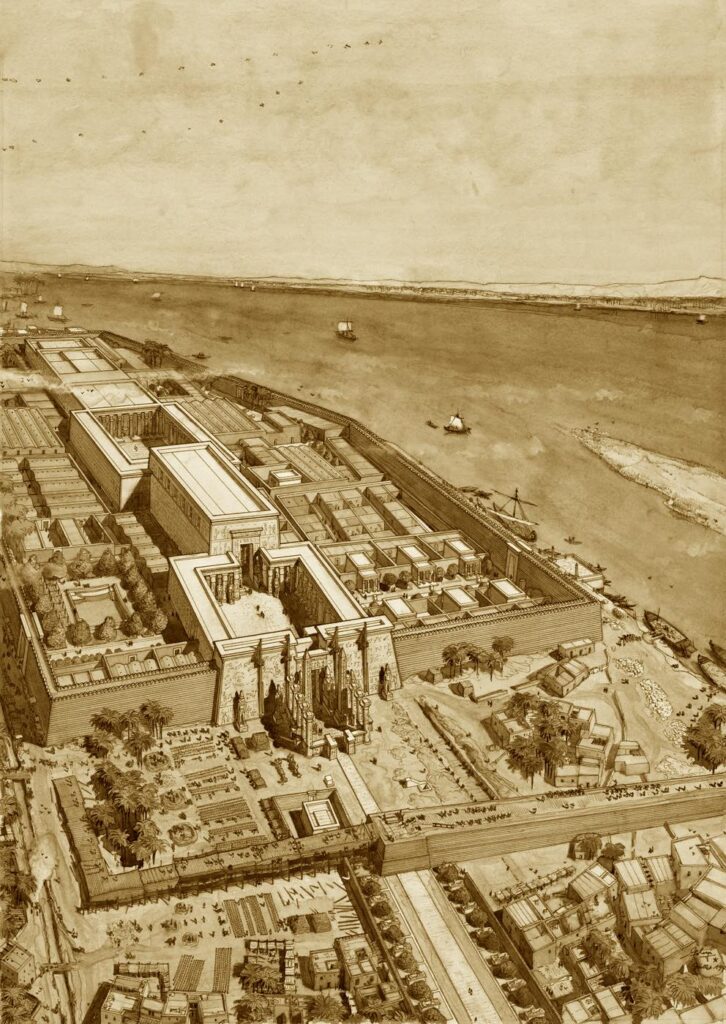
The significance of these museums is profound. They stand as a testament to the rich and diverse history of Egypt, with the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities located in the heart of Cairo, a modern metropolis with a vibrant past. Luxor Museum, conversely, is nestled amongst some of Egypt’s most significant archaeological sites, acting as a cultural hub in a city often referred to as the “world’s greatest open-air museum”.
The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities has played a significant role in Egyptology. It has offered generations of scholars unique research opportunities and has contributed to numerous discoveries and advancements in the field. The museum’s extensive collection covers almost every period of Ancient Egyptian history, providing a comprehensive overview of Egypt’s ancient civilization.
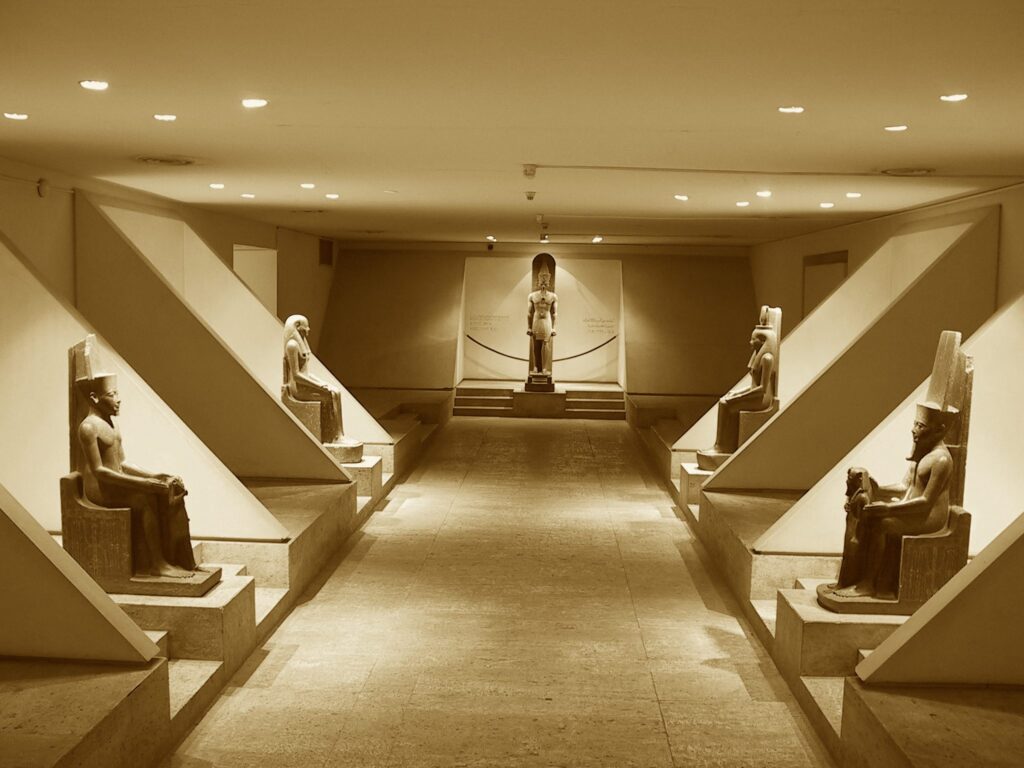
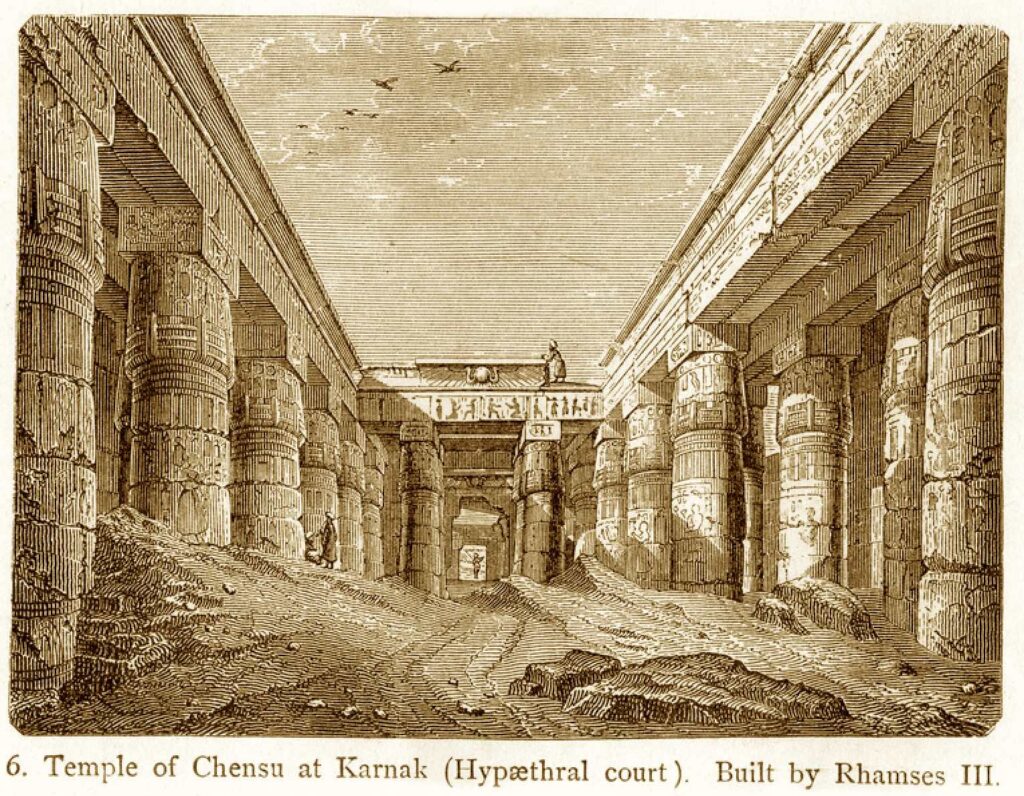
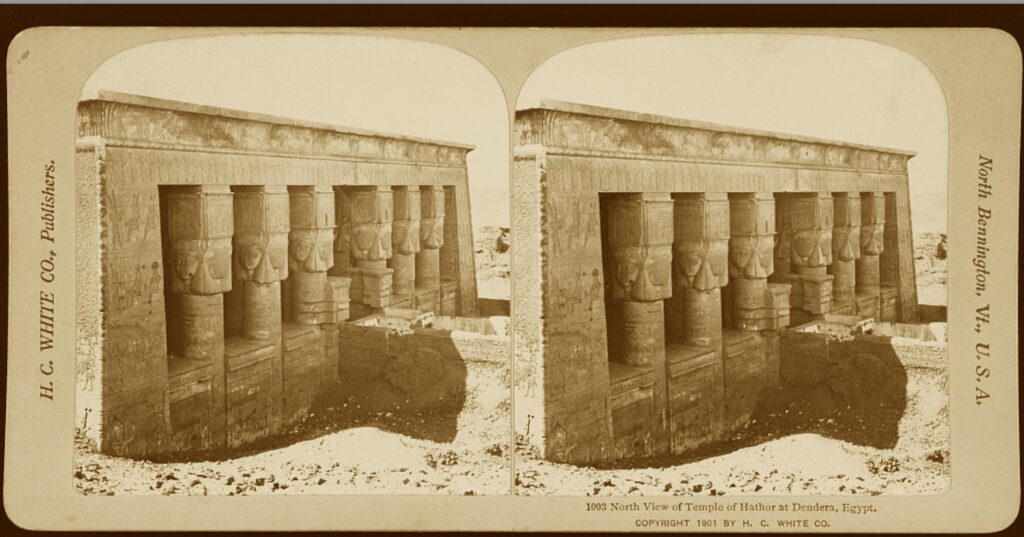
Similarly, the Luxor Museum holds importance in its focus on artifacts from the Theban area, providing in-depth insights into the region’s history. The quality of the items on display and their excellent preservation state makes Luxor Museum a destination for anyone seeking a more intimate understanding of Ancient Egypt.
In summary of The Majesty of Egypt: Luxor Museum vs Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, both the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities and the Luxor Museum are fundamental to Egypt’s cultural heritage. They offer glimpses into the past and contribute immensely to the study and understanding of one of the world’s oldest civilizations.
The Most Notable Artifacts in the Luxor Museum and the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities
In the Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, the golden treasures of the boy-king Tutankhamun indisputably steal the show. Among these incredible finds, the solid gold death mask of Tutankhamun, adorned with semi-precious stones, is one of the most iconic artifacts of ancient Egypt. The mask, discovered in his tomb in the Valley of the Kings, weighs about 11 kg and depicts the pharaoh’s extraordinarily detailed face.
However, Tutankhamun’s treasure is far from being the museum’s only attraction. The museum houses approximately 120,000 items. Another essential piece is the Narmer Palette, a significant relic from the Early Dynastic period. It is considered one of the first historical documents in the world and signifies the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Narmer.